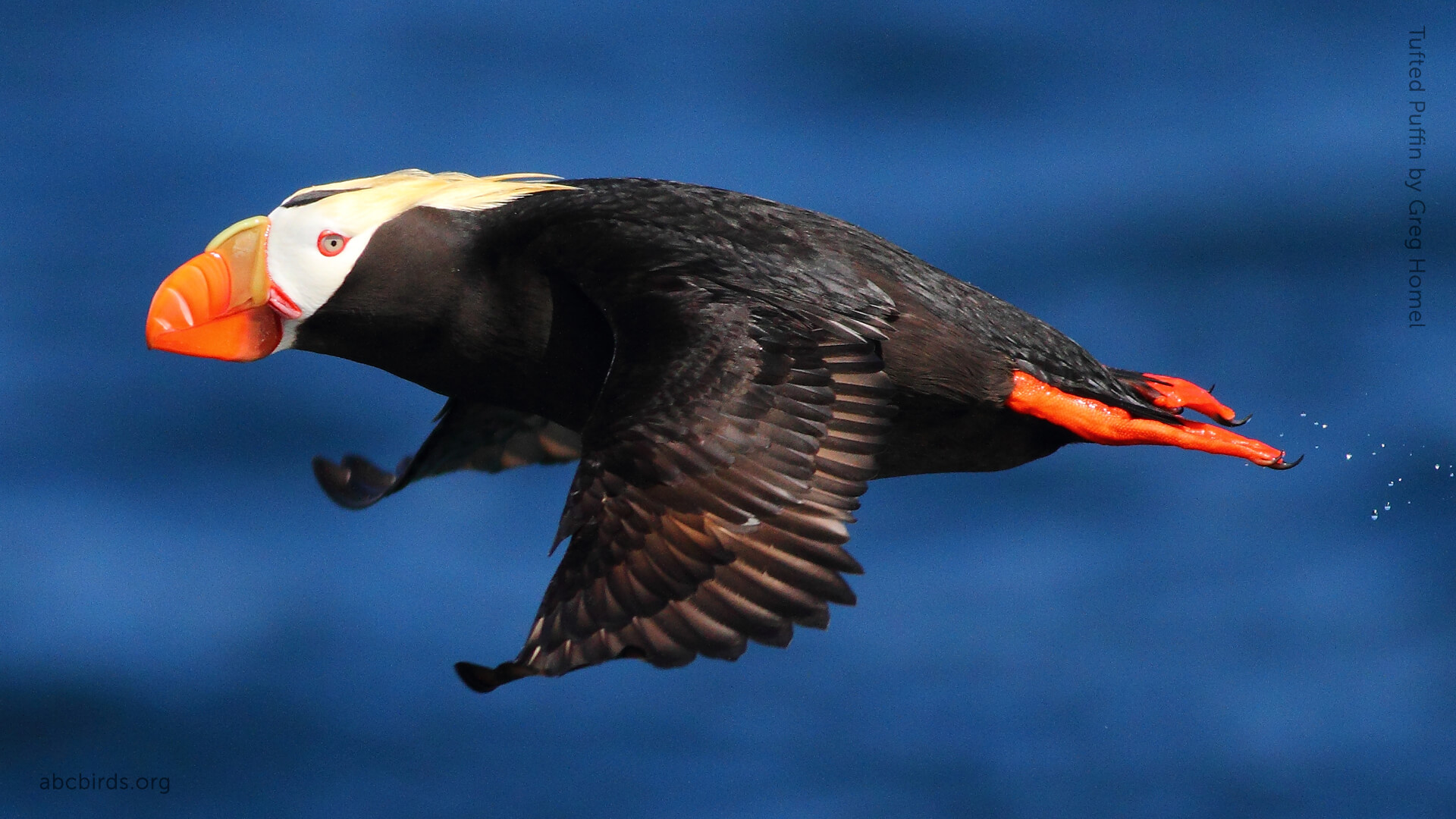
 This distinctive member of the auk family is larger than other puffin species, but the species is best differentiated by its bold white mask and golden head plumes in the breeding season.
This distinctive member of the auk family is larger than other puffin species, but the species is best differentiated by its bold white mask and golden head plumes in the breeding season.
As with other members of the family Alcidae (web-footed diving birds), the Tufted Puffin's wings are relatively short and adapted for swimming underwater. Even so, puffins are powerful flyers, beating their wings 300-400 times a minute and reaching speeds up to 40 miles per hour.
Sadly, bycatch in fishing nets kills thousands of Tufted Puffins and other seabirds, such as Marbled Murrelet, Pigeon Guillemot, and Common Murre, each year.
Fisheries are depleting the Tufted Puffin's main sources of food, small species known as “forage fish.” Competition for forage fish is growing as people harvest them for livestock feed in addition to taking fish for human consumption.
Dual Threat: Overfishing and Climate Change
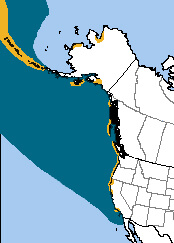
Changes in the distribution and abundance of forage fish due to overfishing and climate change are apparently causing declines in southern populations of Tufted Puffin, while increasing northern populations as birds shift their range northward.
In addition, plastic trash in the ocean is often mistaken for food by hungry puffins and other seabirds, which risk starvation when they fill up on undigestible plastic instead of fish.
Sign up for ABC's eNews to learn how you can help protect birds
Nesting Tufted Puffins are vulnerable to introduced predators such as rats and foxes. Such predators were once absent from most offshore islands in the northeast Pacific, and the puffins have no defense against them.

Tufted Puffin in burrow by Maksimillian, Shutterstock
Amazing Adaptations
Tufted Puffins nest in dense breeding colonies, forming long-term pair bonds to care for their young. The birds dig burrows up to five feet deep into cliff edges and slopes; their beaks and feet are specialized for this excavation work.
Another adaptation, heavy bones, allows the Tufted Puffin to dive up to 200 feet in pursuit of prey, mostly fish and squid; the birds can stay underwater for more than a minute. With “denticles” on the roof of their mouths and a locking tongue, the birds are able grab and hold 5 to 20 small fish crosswise for delivery to chicks at the nest.
Efforts for Puffins and Other Seabirds
ABC has developed a free, interactive mapping and information tool to help fishers and fisheries managers assess their risk of seabird bycatch and take appropriate measures to minimize or eliminate bycatch in their operations.
In addition, ABC-supported programs to eradicate introduced mammals on nesting islands—like this one on Anacapa Island off the coast of California—have led to dramatic recovery of puffin and other seabird populations.
Donate to support ABC's conservation mission!